DW(G) Series
Characteristics of DW, DWG pumps
- Non-self-priming vertical multi-stage pump application
- Stainless steel is applied to the parts in contact with the fluid (to prevent water contamination - except for the DW model)
- Simplified structure where the suction and discharge diameters of the pump are located in the same straight line
- Low noise, low vibration, and excellent durability due to precise balancing
- Easy installation space due to vertical connection structure of the pump and motor
- Split coupling applied to the pump shaft and motor shaft
- Cartridge-type mechanical seal applied to prevent leakage and easy maintenance
- Can be used as an inverter pump capable of rotation speed control
Standard Type

Available Fluids
- Fluids without solid particles or fibrous components
- Fluids with low viscosity
- Fluids that do not cause damage (corrosion) to pump materials and components
Motor specifications
| Model | IEC-Standard squirrel cage type three-phase motor |
| Cooling | Totally enclosed fan cooling (TEFC) |
| Protection class | IP55 |
| Insulation class | F |
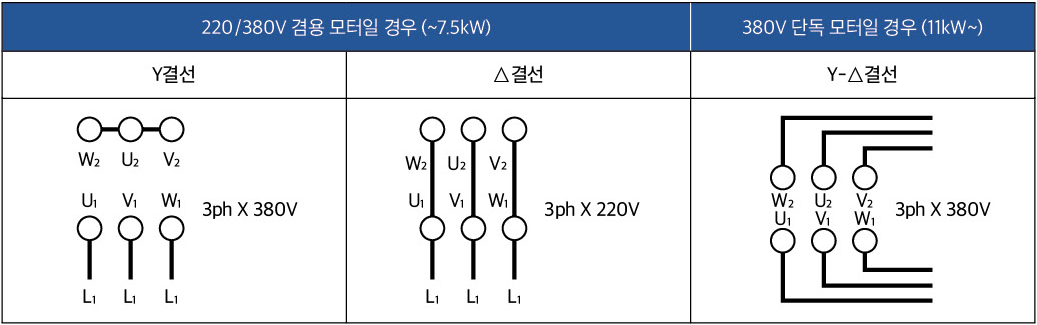
| Power specifications | 7.5kW and below - 3Ph, 220/380V, 60Hz 11kW and above - 3Ph, 380V, 60Hz |
Applications
- Water supply and pressurization equipment
- Water supply for waterworks facilities
- Industrial water supply pressurization
- Washing and cleaning systems
- Water treatment systems
- Sprinkler and fire extinguisher equipment
- Boiler water supply systems
- Industrial circulation pumps
- Cooling and air conditioning systems
- Beverage manufacturing equipment
- Manufacturing process equipment
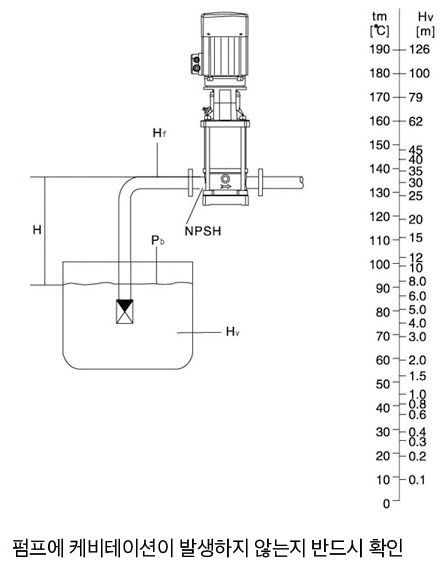
Minimum Suction Pressure - NPSH
In the following cases, the suction head "H" must be checked:
- When the temperature of the liquid being used is significantly high
- When the flow rate being used is significantly higher than the rated flow rate of the pumpWhen water is being sucked
- When the suction side piping of the pump is very long
- When the suction side pressure of the pump is low
To prevent cavitation, the minimum suction pressure must be set on the pump, and the suction head "H" of the pump can be calculated using the following formula:
- H
- = Pb x 10.2 - NPSH - Hf - HV - Hs
- Pb
- = Atmospheric pressure (Atmospheric pressure is specified as 1 bar)
In the case of a closed system, Pb refers to the pressure within the system
- NPSH
- = Maximum suction head
(NPSH value applied when the maximum flow rate is used during pump operation)
- Hf
- = Friction loss in the suction pipe
(value at maximum flow rate when the pump is running)
- Hv
- = Saturated Vapor Armor
(This value is read from the Vapor Pressure Scale. HV varies with the temperature of the liquid (tm))
- Hs
- = Safety factor (minimum 0.5M or more)
If the calculated H value is (+), suction is possible as much as "H"
If the calculated value is (-), pressurization is required as much as "H"
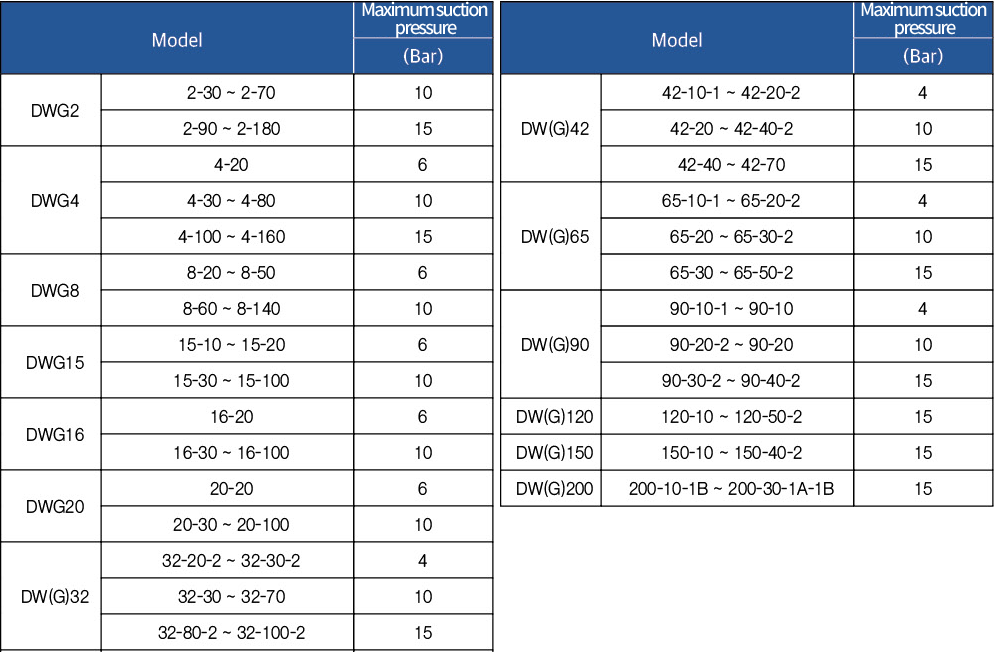
Maximum allowable suction pressure
The table below shows the maximum allowable suction pressure for each pump.Also, the cutoff pressure (pressure of the pump with the discharge valve completely closed) + actual suction pressure must not exceed the maximum allowable operating pressure of the pump.(Cutoff pressure + actual suction pressure) < (maximum allowable operating pressure) If this is exceeded, the motor bearings, shaft seals, or pump housing may be damaged or their service life may be shortened.
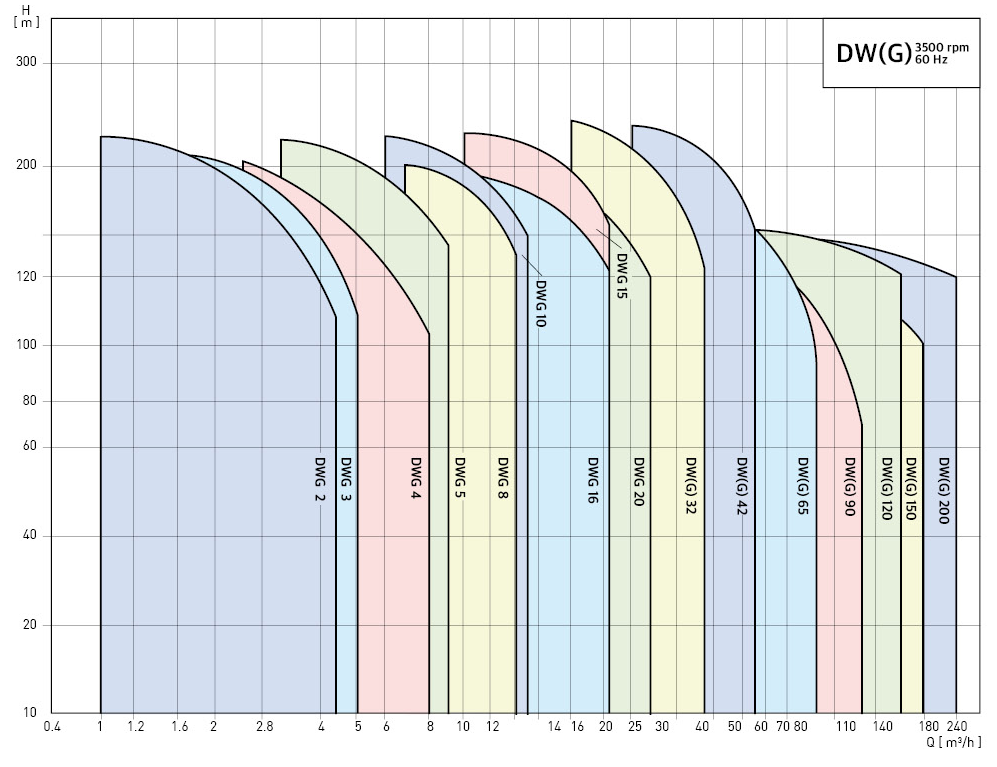
Performance range
Standard specifications
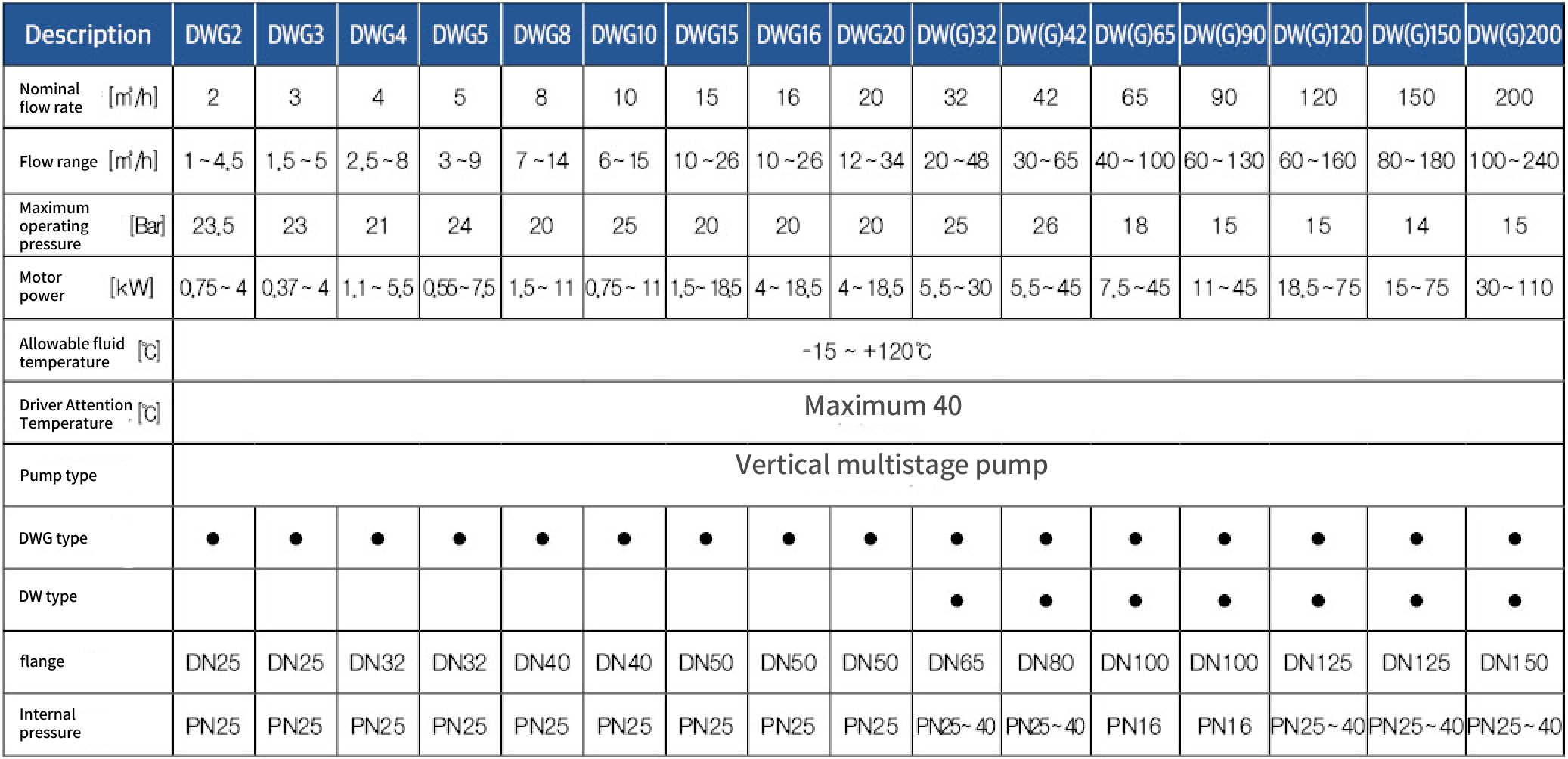
Performance Curve Description
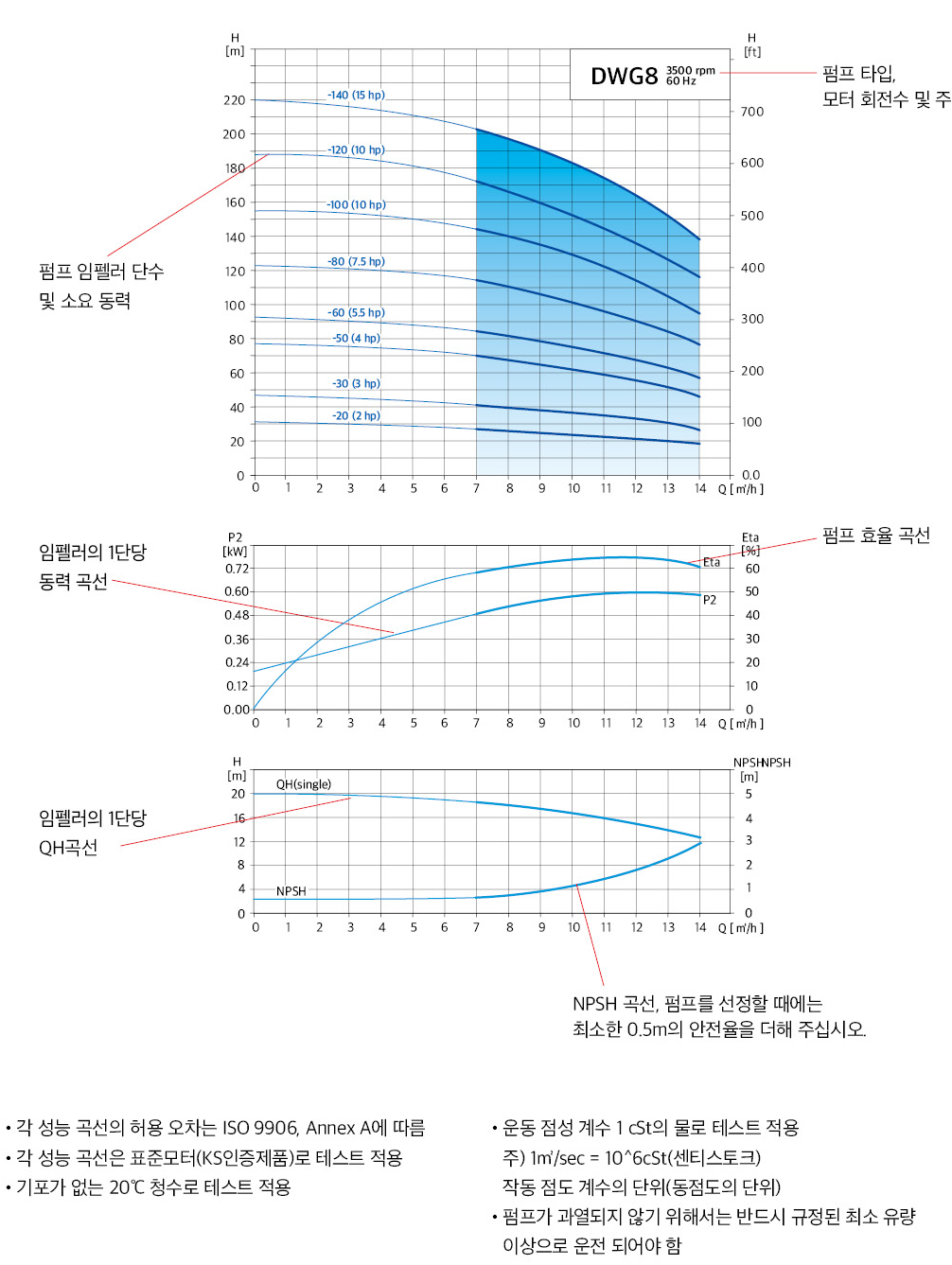
Minimum flow rate
The graph below shows the ratio of minimum flow rate to nominal flow rate as a function of temperature.
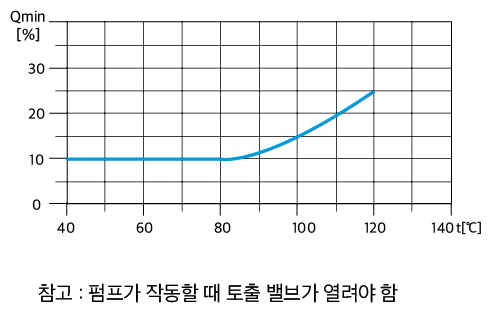
Ambient temperature
When installing the pump at an ambient temperature and height exceeding the rated temperature, the motor output (P2) should be kept lower than the rated output to account for the reduced cooling performance due to the low density of the air, and in some cases, a motor with one order of magnitude greater power should be used.
If the fluid has a higher density and viscosity than water, pump performance will deteriorate (pressure and flow rate will decrease) and power consumption will also increase. In this case, a pump and motor with a larger capacity must be selected.
Motor terminal box location
Motor connection diagram